Hello everyone, we at Nomadev AI, back with another blog of our series WTF IS AI?
Welcome to Day 4 of our 30-day series on Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Generative AI.
No jargon, no buzzwords, just practical, beginner-friendly explanations to help you get the hang of AI one step at a time.
Today, we’ll explore Classification Models in Machine Learning, a cornerstone technique for predicting continuous values.
This blog will explain the concept and guide you through real-world examples, implementation, and applications.
By the end of this blog, you’ll understand how Classification Models in Machine Learning work, their **types, and how to implement them to solve real-world problems.
Let’s roll up our sleeves and dive right in!
What is Classification in Machine Learning?
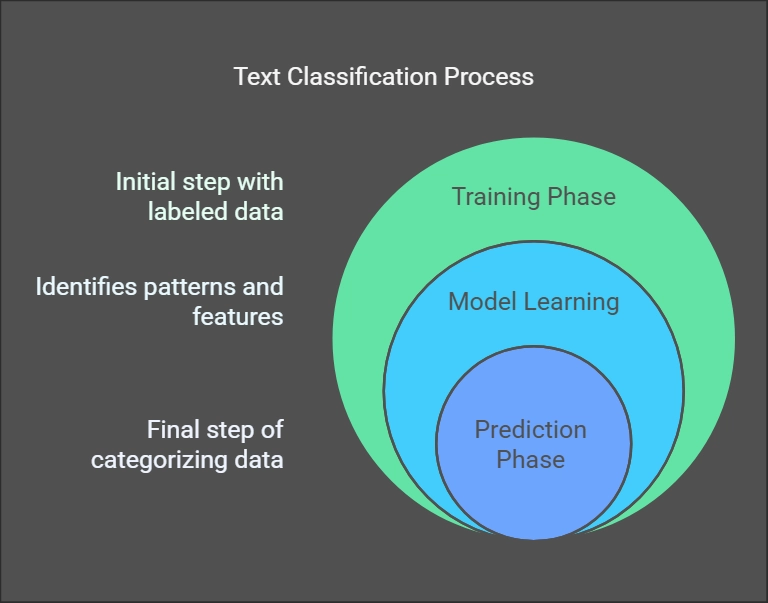
Classification is a type of Supervised Learning where a machine learns to categorize data into different groups or labels based on past examples. The model is trained on labeled data and then predicts the correct category for new data.
Why Classification Models Matter
Classification models help machines make decisions by sorting data into predefined categories. Here’s why they’re essential:
- Spam detection: Automatically identify and block unwanted emails.
- Medical diagnosis: Classify patient data to detect diseases.
- Sentiment analysis: Categorize customer feedback as positive, neutral, or negative.
- Image recognition: Identify objects, faces, or scenes in images.
From making everyday tasks smoother to saving lives, classification models are the backbone of many AI applications.
Types of Classification Models
Classification models vary based on their approach and complexity. Here are some popular ones:
1. Logistic Regression
A simple yet powerful model used for binary classification tasks.
Example: Predicting whether an email is spam (1) or not spam (0).
2. Decision Trees
A tree-like structure that splits data into branches based on conditions.
Example: Classifying customers as high-risk or low-risk based on credit history.
3. Random Forest
An ensemble of decision trees that improves accuracy by averaging predictions.
Example: Predicting whether a loan application will be approved or rejected.
4. Support Vector Machines (SVM)
Finds the optimal boundary (hyperplane) to separate classes.
Example: Classifying handwritten digits.
5. Neural Networks
Powerful models capable of handling complex classification tasks by mimicking the human brain.
Example: Facial recognition in social media apps.
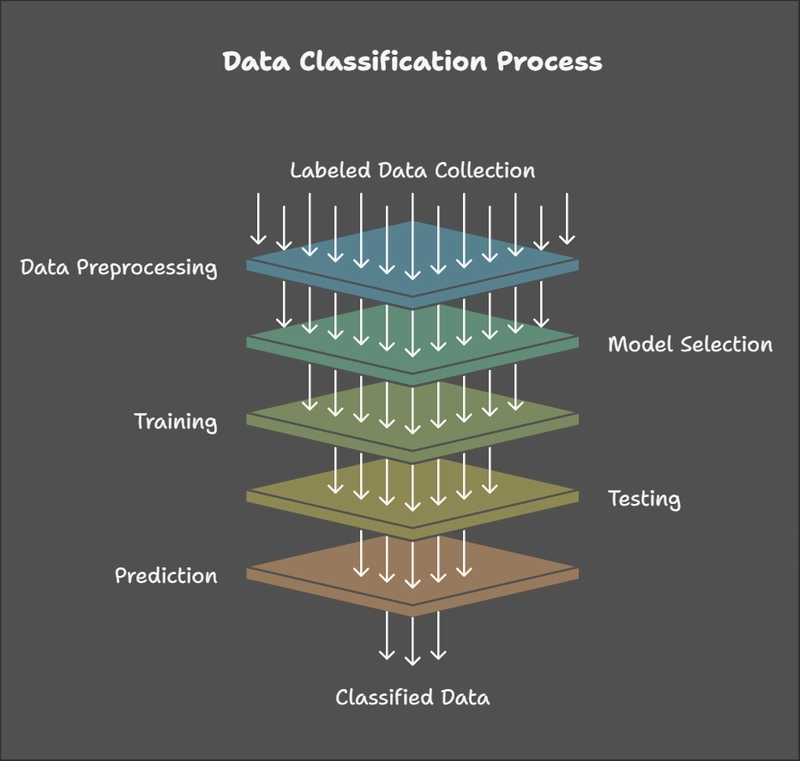
How Classification Works
The classification process involves several steps. Here’s a breakdown:
Step 1: Data Collection
Gather labeled data where each input is associated with a category. Example: emails labeled as spam or not spam.
Step 2: Data Preprocessing
Clean and prepare the data by removing duplicates, handling missing values, and encoding categorical features.
Step 3: Model Selection
Choose the right model for your task (e.g., logistic regression for binary tasks, decision trees for interpretability).
Step 4: Training
Feed the labeled data into the chosen model to learn patterns and relationships.
Step 5: Testing
Evaluate the model on unseen data using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score.
Step 6: Prediction
Deploy the trained model to classify new data into categories.
Example Code
Here’s a simple classification example using logistic regression in Python:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
# Sample data
X = [[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]] # Features
y = [0, 0, 0, 1, 1] # Labels (0: not spam, 1: spam)
# Split data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# Train model
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Test model
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, predictions))
print("Classification Report:\n", classification_report(y_test, predictions))
Real-World Applications
Classification models have revolutionized numerous industries:
- Healthcare: Diagnosing diseases like diabetes or cancer.
- Finance: Fraud detection in credit card transactions.
- Retail: Customer segmentation for personalized marketing.
- Social Media: Content moderation (e.g., detecting offensive posts).
- Technology: Speech recognition in virtual assistants.
These models enable automation and efficiency, driving innovation across sectors.
Metrics to Evaluate Classification Models
Choosing the right metrics is crucial for evaluating model performance. Here are some commonly used metrics:
- Accuracy: Percentage of correct predictions.
- Precision: Focuses on the relevance of positive predictions.
- Recall: Measures how well the model identifies all relevant instances.
- F1-Score: Harmonic mean of precision and recall.
Each metric provides unique insights and is suited to specific scenarios.
Thanks for Joining the Journey!
Thanks for exploring Classification Models with me today! We’ve covered their types, how they work, and real-world applications. This is just Day 4, and we’re steadily building our ML foundations.
What’s Coming Up Next?
Later this week, we’ll explore:
- Day 5: What is Unsupervised Learning?
- Day 6: Introduction to Reinforcement Learning → Understand agents, environments, and rewards—and see it in action.
- Day 7: Data Preprocessing in ML → Discover how to clean, scale, and encode your data for better results.
Let’s Connect and Build Together 🤝
Make sure to follow me on X (formerly Twitter) and turn on notifications to stay updated on all the latest tutorials.
Together, we’ll make AI accessible and fun for everyone.
Here’s how we can collaborate:
✅ Open to DevRel partnerships to help brands grow through educational content.
✅ Have an AI MVP idea or need consultancy services for AI-based applications and research projects? Let’s make it happen!
📧 Drop a mail at: thenomadevel@gmail.com









Top comments (1)
It provides the valuable insight into the core concept of machine learning.